场景
在上一篇文章中,我们创建了一个分区缓存,并开发了一个基本的网格缓存框架。在本文中,我们将与现有数据库集成并使用缓存读取/写入数据。
在使用网格缓存之前,某些应用程序已经具有现有数据库、数据访问机制和数据对象。在本文中,我们将
- 使用具有单个表的现有数据库 (MySQL)
Product。 - 使用产品数据对象类读取和写入数据。
- 构建配置并开发Ignite代码,以将数据读取和写入数据库
- 开发客户端代码以与 Ignite 缓存集成。因此,客户端代码将不知道基础数据库。
这种情况下在大型应用程序中可能很有用,因为所有组件尚未迁移到 Ignite,或者由于技术挑战或应用程序的某些组件的不同策略而无法迁移以点燃。
您可能还喜欢:开始与Apache点火(第1部分)。
现有应用程序详细信息
本节将提供有关我们将在其中使用网格缓存的现有应用程序的详细信息。
数据库
以下是数据库表结构:
|
Id |
名字 |
分类 |
|
1 |
橙 |
水果 |
|
2 |
苹果 |
水果 |
|
3 |
葡萄 |
水果 |
CREATE TABLE `product` (
`id` varchar(100) NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
`classification` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
数据对象
以下是产品表的数据类;此类的每个实例表示产品表中的一行。
/**
* This is data object class. This will be value in the cache.
*/
package com.learning.ignite.dataobject;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* @author Chintan
*
*/
public class Product implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3506766972673961325L;
private String id;
private String name;
private String classification;
public Product(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getClassification() {
return classification;
}
public void setClassification(String classification) {
this.classification = classification;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
}与现有数据库的缓存集成
在本节中,我们将开发与 Ignite 相关的各种配置和代码。然后,我们将缓存与RDBMS集成。
服务器缓存配置
以下是缓存的配置。我已经在XML代码之后描述了配置的细节。
<?xml version="1springframework.org/schema/beans”
xmlns:xsi=”http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema实例”
xsi:架构定位*”
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/bean/春豆.xsd”>
<!–缓存配置 – >
<bean id=”内存网格中.cfg”
类=”org.apache.ignite.配置.点火配置”>
<属性名称=”缓存配置”>
<列表>
<豆
类=”org.apache.ignite.配置.缓存配置”>
<属性名称=”名称”值=”产品缓存” />
<属性名称=”缓存模式”值=”已删除” />
<属性名称=”备份”值=”1″/>
<属性名称=”原子性模式”值=”ATOMIC” />
<属性名称=”写入同步模式”
值=”FULL_SYNC” />
<属性名称=”组名”值=”组1″ />
<属性名称=”通过”值”读取”true”></属性>
<属性名称=”通过”值”写入”true”></属性>
<属性名称=”缓存存储工厂”>
<bean 类=”javax.cache.配置.工厂构建器”
工厂方法=”工厂”>
<构造函数-arg
值=”com.learning.ignite.store.jdbc.productStore”></构造器-arg>
</bean>
</属性>
<属性名称=”查询实体”>
<列表>
<bean 类=”org.apache.ignite.cache.queryEntity”>
<属性名称=”键类型”值=”java.lang.String”></属性>
<属性名称=”值类型”
值=”com.learning.ignite.dataobject.产品”></属性>
<属性名称=”字段”>
<地图>
<条目键=”id”值=”java.lang.String”></条目>
<条目键=”名称”值=”java.lang.String”></条目>
<条目键=”分类”值=”java.lang.String”></条目>
</map>
</属性>
</bean>
</列表>
</属性>
</bean>
</列表>
</属性>
</bean>
<豆
类=”org.springframework.jdbc.数据源.DriverManager数据源”
id=”数据源”>
<属性名称=”驱动程序类名称”
值=”com.mysql.jdbc.Driver”></属性>
<属性名称=”url”
值=”jdbc:mysql://本地主机:3306/萨基拉” />
<属性名称=”用户名”值=”用户1″ />
<属性名称=”密码”值=”某个密码” />
</bean>
</bean>
- 数据库配置:数据库配置在
dataSourceBean 中添加。这将提供数据库的详细信息,如数据库名称、用户 ID、密码、JDBC URL 等。Ignite 将使用它读取和写入数据库中的对象。Ignite 将使用ProductStore类(Java 代码读取/写入/写入数据库)。我在ProdsuctStore下一节中作了详细的解释。 - 读出和写入属性:这是缓存的两个属性。我们需要将它们设置为 true,以确保 Cache 能够读取和写入数据。
- <属性名称=”通过”值”读取”true”></属性>
- <属性名称=”通过”值”写入”true”></属性>
- 缓存存储工厂:此配置将提供
Database StoreJava 类的详细信息。 - 查询实体:此配置将提供存储在缓存中的各种对象的详细信息。此配置将提供键和值。
产品商店
本节将提供有关存储类的详细信息。Ignite 将使用此存储类在数据库中读取和写入。此存储类具有各种方法,包括 load write 、 和 writeAll 。几个要点:
load当缓存中不存在对象时,将调用该方法,并且 Ignite 需要从数据库加载该对象。- 该方法
write将用于将数据写入数据库
package com.learning.ignite.store.jdbc;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.cache.Cache.Entry;
import javax.cache.integration.CacheLoaderException;
import javax.cache.integration.CacheWriterException;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.apache.ignite.cache.store.CacheStore;
import org.apache.ignite.lang.IgniteBiInClosure;
import org.apache.ignite.resources.SpringResource;
import com.learning.ignite.dataobject.Product;
public class ProductStore implements CacheStore<String, Product> {
@SpringResource(resourceName = "dataSource")
private DataSource dataSource;
/**
* This will load the cache object from Cache object
*/
public Product load(String key) throws CacheLoaderException {
System.out.println("Load method is invoked...");
Product product = null;
try {
String sql = "SELECT * FROM PRODUCT WHERE ID = ?";
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
PreparedStatement pStmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pStmt.setInt(1, Integer.parseInt(key));
ResultSet rs = pStmt.executeQuery();
System.out.println("Executed Query.");
while (rs.next()) {
String id = rs.getString(1);
System.out.println("Got result set for " + id);
product = new Product(id);
String name = rs.getString(2);
String classification = rs.getString(3);
product.setName(name);
product.setClassification(classification);
}
} catch (SQLException exp) {
exp.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception exp) {
exp.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("returning result");
return product;
}
public Map<String, Product> loadAll(Iterable<? extends String> keys) throws CacheLoaderException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
/**
* This will write rows in tables from Cache
*/
public void write(Entry<? extends String, ? extends Product> entry) throws CacheWriterException {
System.out.println("Enterring in write method. ");
try {
String sql = "INSERT INTO PRODUCT VALUES (?, ?, ?)";
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
PreparedStatement pStmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
System.out.println("Opened database connection..");
String id = entry.getKey();
String name = ((Product)entry.getValue()).getName();
String classification = ((Product)entry.getValue()).getClassification();
System.out.println("Got values from passed object.");
pStmt.setString(1, id);
pStmt.setString(2, name);
pStmt.setString(3, classification);
pStmt.execute();
System.out.println("Inserted objects.");
} catch (SQLException exp) {
exp.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception exp) {
System.out.println("Exception while writing data.");
exp.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* This will write objects in bulk in database.
*/
public void writeAll(Collection<Entry<? extends String, ? extends Product>> entries) throws CacheWriterException {
try {
String sql = "INSERT INTO PRODUCT VALUES (?, ?, ?)";
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
PreparedStatement pStmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
Iterator<Entry<? extends String, ? extends Product>> itr = entries.iterator();
while (itr.hasNext()) {
Product entry = (Product) itr.next();
String id = ((Product) entry).getId();
String name = ((Product) entry).getName();
String classification = ((Product) entry).getClassification();
pStmt.setString(1, id);
pStmt.setString(2, name);
pStmt.setString(3, classification);
pStmt.execute();
}
} catch (SQLException exp) {
exp.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception exp) {
exp.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void delete(Object key) throws CacheWriterException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
public void deleteAll(Collection<?> keys) throws CacheWriterException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
/**
* This will load all objects from database to cache
*/
public void loadCache(IgniteBiInClosure<String, Product> clo, Object.args) 引发缓存加载器异常 |
System.out.println(”调用加载方法…”);
产品 = 空;
尝试 |
字符串 sql = “选择 = 从产品”;
连接连接 = 数据源.getConnect();
准备语句 pStmt = conn.prepared 语句(sql);
结果集 rs = pStmt.执行查询();
而 (rs.next()) |
字符串 ID = rs.getString(1);
产品 = 新产品(id);
字符串名称 = rs.getString(2);
字符串分类 = rs.getString(3);
产品.setName(名称);
产品.集分类(分类);
clo.apply(String.valueof(id),产品);
}
• 捕获 (SQLException exp) *
exp.printStackTrace();
[ 渔获量 (例外 exp) ]
exp.printStackTrace();
}
}
公共无效会话结束(布尔提交)引发缓存文件异常 |
TODO 自动生成的方法存根
}
}
客户端点火配置
以下是客户端的 XML 配置。我保持客户端配置分开,因为客户端可能不是同一应用程序的一部分。客户端可以是完全不同的应用程序。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- Configuration of Cache -->
<bean id="client-memory-grid.cfg"
class="org.apache.ignite.configuration.IgniteConfiguration">
</bean>
<bean
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"
id="dataSource">
<property name="driverClassName"
value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url"
value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/sakila" />
<property name="username" value="user" />
<property name="password" value="password" />
</bean>
</beans>
客户代码
这是来自客户端的示例代码。此代码将访问 Product Cache 并将放置一些对象并获取一些对象。
package com.learning.ignite.node;
import org.apache.ignite.Ignite;
import org.apache.ignite.IgniteCache;
import org.apache.ignite.Ignition;
import com.learning.ignite.dataobject.Product;
/**
* This is Ignite Cache Client. This class will put and get objects from Cache
* Server.
*
* @author chintan
*
*/
public class CacheClient {
public static String cacheName = "ProductsCache";
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Starting Cache Client");
/*
* Set the mode of the client. This can also be done by creating XML
* configuration.
*
* In this case, my server and clients are running on same machine. Hence, I
* have not provided network discovery related configuration. In most cases, the
* client node will run on different machine. in this case, we need to pass the
* network configuration like static IP address or multicast IP address. in
* general, I prefer to use multicast IP address to make sure that multiple
* clients & servers are able to connect and there is no dependency on actual IP
* address. s
*
*/
Ignition.setClientMode(true);
Ignite ignite = Ignition.start("F:\\Installed\\apache-ignite-2.7.6-bin\\config\\client-config.xml");
System.out.println("Client Node Started..");
// The Cache name
IgniteCache<String, Product> cache = ignite.cache(CacheClient.cacheName);
System.out.println("Got instance of Cache " + CacheClient.cacheName);
// Store keys in cache (values will end up on different cache nodes).
for (int i = 21; i <= 30; i++) {
Product prdObject = new Product(String.valueOf(i));
prdObject.setName("Product Name = " + i);
prdObject.setClassification("classification" + i);
cache.put(String.valueOf(prdObject.getId()), prdObject);
}
System.out.println("Added Objects in Cache");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("trying to get object for " + i);
Product prd = cache值of(i));
如果 (prd != 空)
System.out.println(”从缓存接收对象” = prd);
还
System.out.println(”对象为空”);
}
}
}
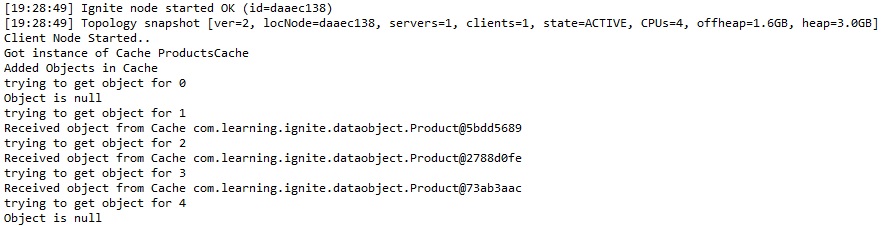
控制台输出
数据库表
如下表所示,数据库表具有其他行。这些行由客户端插入。
| Id | 名字 | 分类 |
| 1 | 橙 | 水果 |
| 2 | 苹果 | 水果 |
| 21 | 产品名称 = 21 | 分类21 |
| 22 | 产品名称 = 22 | 分类22 |
| 23 | 产品名称 = 23 | 分类23 |
| 24 | 产品名称 = 24 | 分类24 |
| 25 | 产品名称 = 25 | 分类25 |
| 26 | 产品名称 = 26 | 分类26 |
| 27 | 产品名称 = 27 | 分类27 |
| 28 | 产品名称 = 28 | 分类28 |
| 29 | 产品名称 = 29 | 分类29 |
| 3 | 葡萄 | 水果 |
| 30 | 产品名称 = 30 |
分类30 |
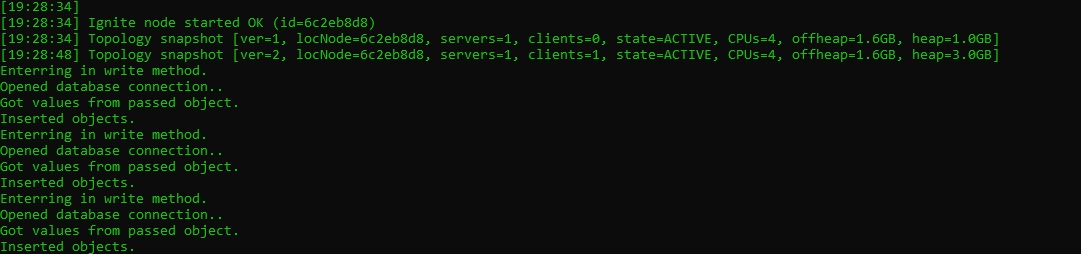
服务器控制台
如下图所示,当缓存对象放置或从缓存获取时,服务器将打印各种 SSP。
客户端控制台
以下是客户端控制台上的输出。这表明它能够从数据库中获取 ID 1、2 和 3 的对象。这些是数据库中的现有行。